302 Response
Contents
- What is an HTTP 302 response?
- How does a 302 redirect work?
- The importance of temporary redirects
- When to use a 302 redirect
- How do 302 redirects affect SEO?
- How to implement 302 redirects on your website
- How do you check your site for the 302 error code?
- Troubleshooting common 302 redirect issues
- Monitoring and optimizing 302 redirects
- FAQ about 302 Response
- Related articles
What is an HTTP 302 response?
An HTTP 302 response is a status code that indicates a temporary redirection. It’s a server’s way of telling your browser that the page you want to visit has been temporarily moved to a different URL.
This type of response is commonly utilized during scenarios such as website maintenance or when the content is temporarily relocated.
How does a 302 redirect work?
When you click a link or type a URL, your browser sends a request to the server. If the page has temporarily moved, the server responds with an HTTP 302 status code and includes the new URL in the 'Location' header of the response. Your browser then automatically goes to this new URL, fetching the page you initially wanted to see.
This process is seamless for the user, who sees only the final content after the browser has followed the redirect to the new address. The use of HTTP 302 is crucial for maintaining user experience during temporary changes to a website's structure or location.
The importance of temporary redirects
Temporary redirects are essential for guiding visitors and search engines to an alternative page when the original is unavailable due to updates or maintenance. Here are a few benefits they offer:
- User experience: Temporary redirects ensure users are seamlessly redirected to the correct resource without encountering errors or dead links.
- Intact SEO rankings: 302 response codes inform search engines that the move is not permanent, preventing potential negative impacts on search engine rankings while still directing traffic appropriately.
- Flexibility in content updates: Temporary redirects allow website administrators to temporarily redirect users to alternative content while the original content is being updated or maintained.
These benefits make 302 redirects a valuable tool for managing web traffic and maintaining website functionality during temporary changes.
When to use a 302 redirect
A 302 redirect is useful in several scenarios where a temporary redirection is appropriate:
Site maintenance: When a website or specific page is undergoing maintenance, a 302 redirect can temporarily direct users to a maintenance page or an alternative page.
Content updates: If a page's content is being updated or revised, a 302 redirect can guide users to a temporary page with relevant information, maintaining content accessibility without altering the original URL structure.
Temporary promotions or events: For time-sensitive promotions, sales, or events, a 302 redirect can direct traffic to a specific landing page for the duration of the event. Once the event ends, the redirect can be removed without affecting the original URL.
A/B testing: To test different versions of a webpage and determine which one performs better, a 302 redirect can temporarily send a portion of the traffic to an alternate version without making permanent changes.
Temporary domain moves: If a site is temporarily moved to a new domain (perhaps during a rebranding process or server migration), a 302 redirect can be used to ensure users are directed to the new domain temporarily until the move is permanent.
How do 302 redirects affect SEO?
HTTP status code 302 affects your site’s SEO in two ways – both positively and negatively.
On the positive side, they inform search engines that the redirection is temporary, which means the original URL is still indexed and ranked. This can be beneficial for short-term changes, ensuring that the original URL's SEO value is maintained while directing users to the temporary content.
Plus, 302 redirects improve the user experience. Instead of seeing a 404 Page Not Found error message, they are imperceptibly redirected to a valid one.
302 response codes also allow the flexibility to revert changes without SEO penalties, which is useful for A/B testing and temporary promotions.
However, on the negative side, if a 302 redirect is mistakenly used for a permanent move, search engines may not transfer the SEO value to the new URL. This potentially causes a loss in rankings and traffic.
How to implement 302 redirects on your website
Implementing 302 redirects on your website might seem challenging, but there are ways to simplify the process. Using plugins and extensions, you can easily manage these redirects. Alternatively, for those who prefer a hands-on approach, manual configuration is also an option.
Let's explore both methods in detail.
Using plugins and extensions
Several plugins and extensions can help you set up 302 redirects easily on your website. For WordPress, popular options include the Advanced 301/302 Redirect and Rank Math SEO, which all provide user-friendly interfaces for managing redirects.
Joomla users can utilize the built-in Redirect Manager or the JRedirects extension for comprehensive URL management. Magento users can take advantage of the Mageworx SEO Suite which offers a variety of SEO functionalities, including managing 301 and 302 redirects.
In Drupal, the Redirect Module is a reliable option for managing 302 redirects. Shopify users aren’t left behind either, with plugins like Easy Redirects, Traffic Control-Bulk Redirects, and Redirect Pro.
Manual configuration
Manual configuration offers full control over the 302 redirect process for webmasters who prefer a hands-on approach. Let’s figure out how to set up 302 redirects for Apache and Nginx servers:
Nginx
To manually configure a 302 redirect on an Nginx server:
- Access the configuration file: Open the appropriate configuration file, typically located at /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or in the sites-available directory.
- Edit the server block: Within the server block, add a location block for the URL you want to redirect. For example:
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location /old-page.html {
return 302 http://www.example.com/new-page.html;
}
}
- Test the configuration: Run sudo nginx -t to check for syntax errors.
- Reload Nginx: Apply the changes with sudo system ctl reload nginx.
Apache
To manually configure a 302 redirect on an Apache server:
- Access the .htaccess file: Open the .htaccess file in your website’s root directory, or the main configuration file if you prefer.
- Add the redirect rule: Add the following line to create a 302 redirect:
- Save the file: Save the changes to the .htaccess file.
- Reload Apache: If you edited the main configuration file, reload Apache with sudo systemctl reload apache2.
By following these steps, you can set up a 302 redirect manually on both Nginx and Apache servers.
How do you check your site for the 302 error code?
Use tools like WebSite Auditor to analyze and check your site’s pages for 302 HTTP status codes. For that, go to Site Structure > Site Audit > Redirects and find all Pages with 302 redirect. Check each page on the list and analyze if all the pages are redirected as intended.
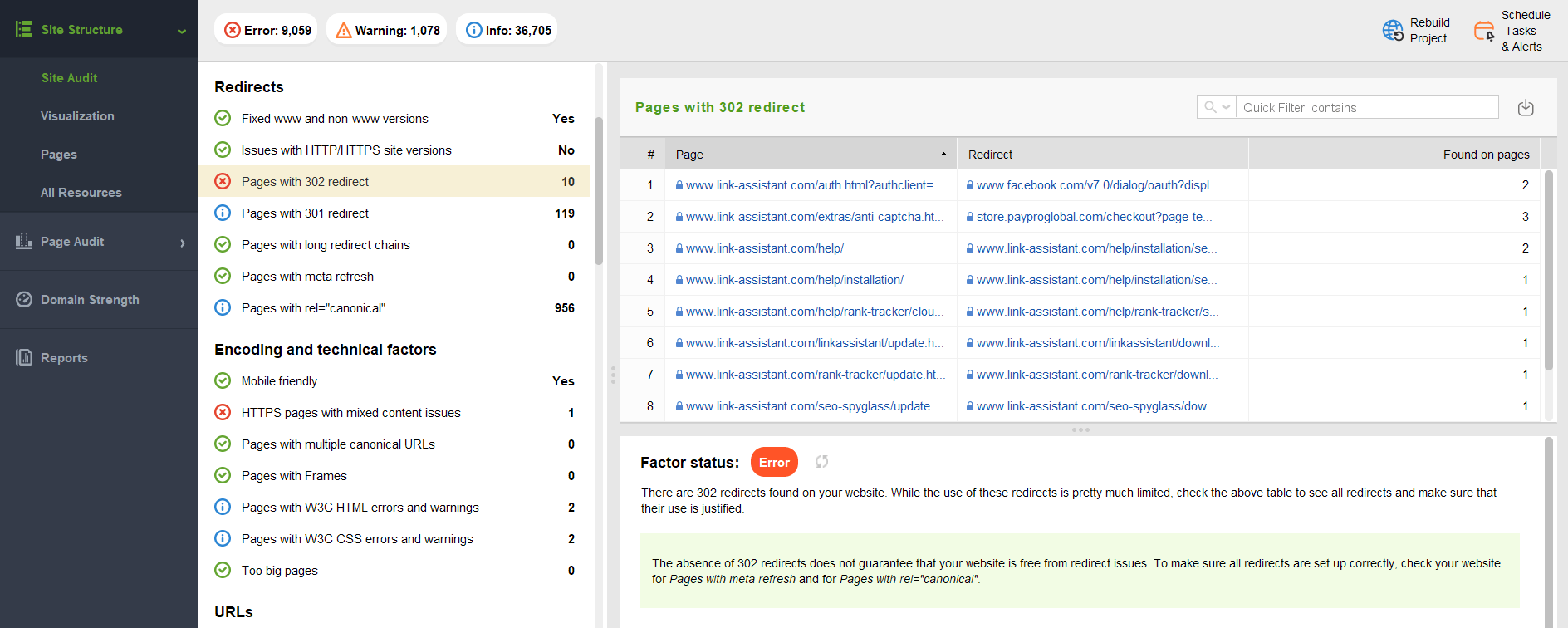
If you use a CMS, there are special plugins for each of them where you can set up and control HTTP status code 302.
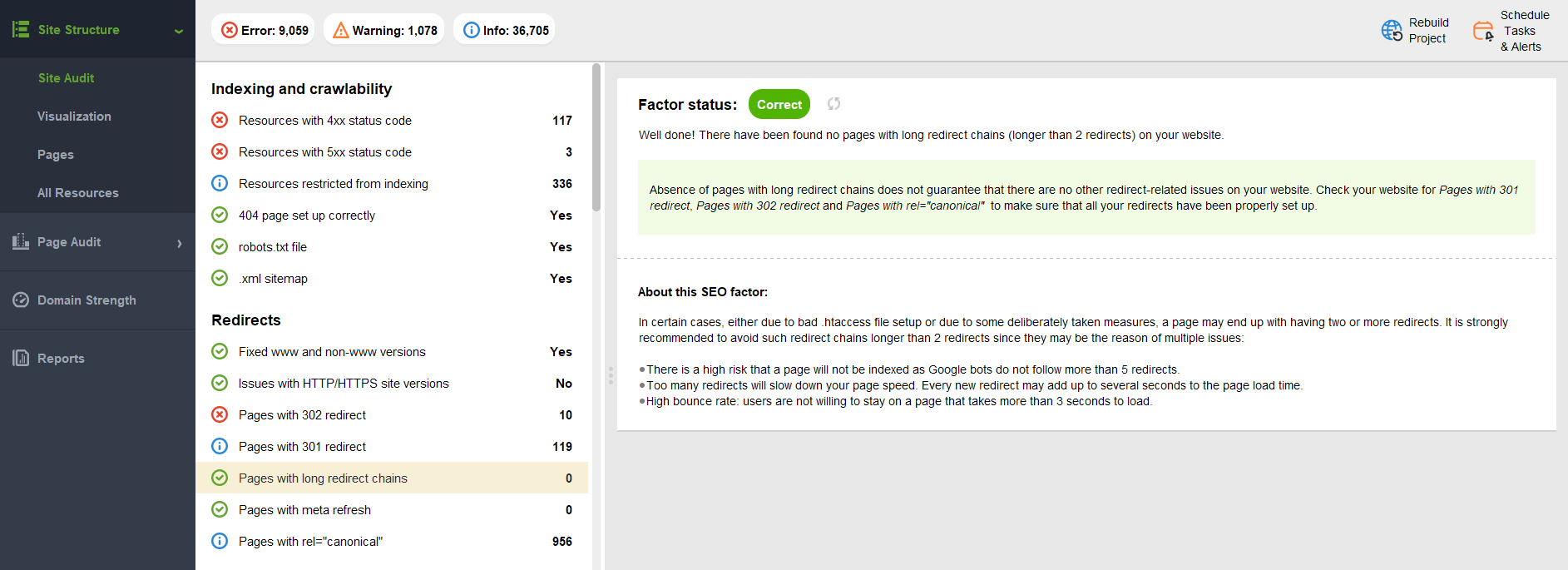
Another issue you should keep track of is redirect chains with code 302. When one page is redirected to the second one, and then the second one to the third one, and so on. It complicates crawling and wastes PageRank. Plus, it may worsen page load time, which is bad for the user experience.
To find such chains of redirects with 302 HTTP status codes, go to Site Structure > Site Audit > Redirects and find Pages with long redirect chains report. Here, you will find information on whether your site faces such an issue.
Troubleshooting common 302 redirect issues
Despite your best efforts, you may encounter issues with 302 redirects. The two most common problems are redirect loops and incorrect URL settings.
We will dissect these problems and offer solutions for each.
Resolving redirect loops
A redirect loop occurs when a series of redirections between URLs create an infinite loop, where a page repeatedly redirects back to itself or between a limited set of pages. This situation typically results in a browser error message indicating that the page is unable to load due to too many redirects.
In this case, you can do the following:
Check redirect configuration: Review your server configuration (.htaccess for Apache or Nginx configuration files) and ensure that the redirect rules are correctly specified.
Clear browser cache: Sometimes, browsers cache redirects. Clear your browser cache and cookies to ensure you're testing the latest configuration.
Inspect network requests: Use browser developer tools (Network tab) to inspect the HTTP requests. Look for multiple consecutive redirects (HTTP 302) that indicate a loop. Identify the source and target URLs involved in the loop.
Use redirect checker tools: Online tools like Redirect Checker or similar can help diagnose redirect loops by showing the sequence of redirects and any potential loops in the chain.
Fixing incorrect URL settings
Incorrect URL settings in 302 redirects can lead to issues like broken links, incorrect redirect settings, resource loading, and configuration problems. These issues can arise from various factors such as configuration errors, plugin conflicts, or a misconfigured web server.
To fix this, take the following steps:
Verify URL syntax: Double-check the syntax and formatting of the URLs in your redirect rules. Ensure they include the correct protocol (http:// or https://) and domain name.
Check for typos: Look for any typos or misspellings in the source or target URLs specified in your redirect rules. Even minor errors can prevent the redirect from functioning correctly.
Use absolute URLs: Always use absolute URLs (e.g., http://www.example.com/new-page.html) rather than relative URLs (/new-page.html) to avoid potential issues with base paths or domains.
Test redirects: Manually test each redirect rule by entering the source URL in a web browser and verifying that it redirects to the correct target URL. Ensure that the redirection occurs as expected without any errors.
Review server logs: Check your server logs for any error messages or warnings related to redirect attempts. Logs can provide insights into why a redirect might be failing or not behaving as expected.
By systematically addressing these common issues, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve 302 redirect problems.
Monitoring and optimizing 302 redirects
After setting up your 302 redirects, monitoring and optimization are vital to ensure optimal performance and avert potential SEO issues. We will examine some tools for monitoring and discuss optimization best practices.
Tools for monitoring redirects
Several tools are available to help monitor 302 redirects, and one of the most popular is the Chrome extension, Redirect Path. This tool flags up 301, 302, 404, and 500 HTTP Status Codes, as well as client-side redirects like Meta and Javascript redirects.
Website monitoring tools like SEO PowerSuite’s WebSite Auditor tool can be invaluable for managing 302 redirects. When choosing a 302 redirect monitoring tool, key attributes to consider include:
- The capacity to add new redirections
- Support for 301 and 302 redirects
- Analysis of common JavaScript redirects
- The ability to check for HTTPS redirects
There are also complimentary tools like Redirect Checker, which are designed to assess HTTP 301 or 302 URL redirects. SEO tools, in general, are highly effective in identifying 302 redirects on a website, and should be considered a valuable part of any webmaster’s toolkit.
Best practices for optimizing temporary redirects
Optimizing 302 redirects is crucial for maintaining SEO performance and user experience during temporary changes. Here are some best practices:
Use 302 redirects appropriately: Use 302 redirects only for temporary situations where the original URL is expected to return in the future. For permanent moves, use 301 redirects instead.
Specify clear timing: If possible, clearly communicate the temporary nature of the redirect by specifying an appropriate expiration date or event completion date. This helps search engines understand when to revert to the original URL.
Monitor and update: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of temporary redirects. Update or remove them promptly when they are no longer needed to prevent unnecessary redirections.
Minimize redirect chains: Avoid creating redirect chains where multiple redirects are linked in sequence. Each additional redirect increases page load time and can negatively impact SEO.
Check mobile and desktop versions: Verify that temporary redirects work correctly across both mobile and desktop versions of your site to ensure a seamless user experience across devices.
Use tools for monitoring: Use tools like Google Search Console or WebSite Auditor to monitor and analyze the performance of your redirects regularly.
FAQ about 302 Response
What is a 302 response?
A 302 response is an HTTP status code that indicates a temporary redirection. It tells the client (such as a web browser or API client) that the requested resource has been temporarily moved to a different URL. Unlike a 301 redirect which is permanent, a 302 redirect implies that the original URL might be accessible again in the future.
Why is my API returning a 302?
Your API might return a 302 response if it is configured to temporarily redirect requests to another endpoint. This could be due to maintenance, load balancing, or temporary changes in resource availability. Ensure your API client can handle and follow these redirects appropriately.
How does a 302 redirect work?
When a server responds with a 302 status code, it includes a "Location" header specifying the URL to which the client should redirect. The client then makes a new request to this URL. Unlike a 301 redirect which is cached by browsers and search engines as permanent, a 302 redirect is typically not cached in the same way because it implies a temporary move.
How can I implement 302 redirects on my website?
You can implement 302 redirects manually through server configuration files like .htaccess for Apache or Nginx configuration files. Alternatively, use plugins and extensions on content management systems (CMS) like WordPress or Joomla for easier management and monitoring.
How can I monitor and optimize 302 redirects?
Monitor 302 redirects using tools like Redirect Checkers, Google Search Console, WebSite Auditor, or browser developer tools (Network tab). Optimize them by ensuring they are used appropriately (temporarily), avoiding creating redirect chains, and updating or removing them promptly when no longer needed.
Should I use 301 or 302 redirect?
Use a 301 redirect for permanent URL moves where the original URL will not be used again. Use a 302 redirect for temporary changes where the original URL might be restored or accessed again in the future.
Are 302 redirects bad for SEO?
302 redirects are not inherently bad for SEO if used correctly for temporary situations. However, improper use or long-term deployment of 302 redirects for what should be permanent changes can confuse search engines and affect SEO negatively. Always use the appropriate redirect type based on the permanence of the change.





