
9 SEO Tips on How to Optimize for Yandex


Breaking news! There ARE search engines besides Google! Ok, I'm kidding, of course, but it is true that a few hugest markets are monopolized or heavily influenced by Google. However, there are still some markets (no less huge) where the first choice for a search query is (tadaaa) not Google. If it so happens that you need to target them, you have to understand optimization peculiarities of a local search engine.
To end this obscure introduction, I would like to ask: have you heard of Yandex? The thing is, if you need to target the Russian-speaking market, this search engine is your first optimization stop. Welcome to an all-expenses paid guide through the anomalies of not only Russian SEO in general, but SEO for Yandex, the king of the industry.
First, the news that will brighten up any gloomy day.
If your site is ranking in Google, and it's technically flawless, then most probably, it will rank in Yandex. However, some ranking factors in Yandex SEO, if missed, can gravely affect your rankings or lead you astray.
A few facts about Yandex.

Yandex started in 1990 when two Russian developers founded Arcadia, a company that developed MS-DOS software for use in patents and goods classification. Their software featured a full-text search with Russian morphology support.
The term Yandex was coined in 1993. It stood for "Yet Another iNDEXer" (I love this hint of sarcasm).
Today, similar to Google, Yandex is not just a search engine, it is a multinational IT company with a wide variety of services and products, including and not limited to:
- Yandex Browser
- Yandex Mail
- Yandex Maps
- Yandex Disk
- Yandex Taxi
- Yandex Translate
- Yandex Market
- Yandex Money
Besides a huge Russian market, Yandex is also extensively used in Belarus, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, and Turkey.
Why optimize for Yandex?
If you want to target the Russian market relying on the fact that your site is optimized for Google, just consider this. In 2017, over 60% of Internet users in Russia chose Yandex to conduct their online searches.
In spite of the fact that Yandex's algorithms are less top-notch than Google's, there are some factors that make it hard for outsiders to fit in.
On the bright side, Yandex has quite a few pros:
+ It is easy to use because it is similar to Google;
+ Though there is less traffic, competition is lower both in the organic and paid search;
+ Less sophisticated algorithms are easier to optimize for;
+ Paid search tends to be less expensive per click;
+ When your site ranks on Yandex, it also ranks on another rather popular Russian search engine — mail.ru;
+ Yandex is far better than Google in indexing sites in Russian, making Russian SEO an absolute breeze for those who can speak Russian;
+ Yandex has a small and responsive customer care team. In case you suspect that your site has suffered a penalty, you can write there, and most likely, you will receive a prompt feedback.
Yandex SEO in a nutshell.
1. Geo-targeting.
It is a known fact that Yandex highly prioritizes geo-targeted searches. While local SEO plays a certain role in most search engines, their users from different parts of the country see more or less similar results. Yandex SEO works a little differently.
All searches there are divided into geo-dependent and geo-independent. Geo-independent ones are common searches, like a book or a recipe. Such queries do not need to be region-based to pull a complete answer.
When it comes to products or services, users from different regions, in most cases, will see different search results.
While this situation creates perfect conditions for promoting a local business, on the flip side, it's more difficult to target multiple locations. However, if your site is optimized for Google, you should know that Google is not really good at telling between specific regions of the CIS countries. With it, you have to target the whole country even if you are interested in one region. Thus, Yandex here is a far better choice.
First of all, determine a region or regions that you want to target. When it is done,
- Indicate your region in Yandex Webmaster Tools;
- Submit your business to Yandex Business Directory;
- You can specify up to 7 regions.
It is not only an IP address that determines your target region. There are a few strategies that can help Yandex search bots render your site for the region that you aim for:
- Include the complete address of your business on your site, like: company's name, country, city, street, postal code, telephone number (plus a city code).
- Specify additional addresses in other regions. If your business is present in a few regions, do not worry, specify all the full addresses, and Yandex robot will figure out that your business covers a few regions.
- Do not hide region-specific content by an IP address. Some sites display different regional versions of the site depending on the user's IP. It is recommended to make all pages accessible to the robot, as it automatically sifts out and delivers the results according to an IP address.
- Make use of subdomains in case your site contains a good amount of information about regional offices. Include region-specific keywords into tags of such subdomains, like in titles and h1-h6 as well as into URLs and content. And make sure a regional subdomain is included into the navigation of the main site.
2. User engagement.

While Google is ingeniously avoiding a direct confirmation that user behavior is a huge influence on rankings, with Yandex — there is no debate. Here, user engagement metrics are an important ranking factor (spoiler: one of several ranking factors far more crucial than backlinks). Those sites that encourage their users to stay longer on them will almost always rank higher than their competitors.
The influence of user experience is especially powerful when it comes to queries with so-called commercial intent. It means that all ecommerce sites should provide impeccable search experience. I'm planning to devote a separate section of the article to this subject, please read on.
What you need to remember from this point is that you should absolutely avoid manipulating user behavior. Yandex is not a newbie to punishing severely.
The blackest-hat techniques that you can apply to make Yandex angry are:
- Use of software and plugins that emulate user behavior, like faking page visits, mimicking internal visits from page to page, creating unnatural comments and spam. The search engine can locate that software and punish the site for crooked methods.
- Use of cheating techniques, like planting malware and viruses that pose a risk to users as well as automatic redirects to third-party resources or downloading another program when the user downloads something else.
- Aggressive display of ads (including pop-ups) — Yandex updated its core algorithm in 2012 and 2014 to spot and punish sites with intrusive pop-up windows that interfere with UX and content accessibility.
Plus, you can monitor user behavior by using Yandex.Metrica and analyzing (regularly) your web server logs.
Pay attention to:
- Sources of traffic
Find out where your users come from and which sources bring most users to your site. An aspect of technical SEO to keep an eye on, in order to better understand your audience. Monitor changes in a report, analyze the behavior of users from new sources, as these new users' behavior may require changes on your part.
- Search queries
Analyze which queries bring visitors to your site, plus, use the report to track new search queries that bring people to you.
- Target pages
Monitor how users perform desired actions on your target pages, like adding an item to the cart, proceeding to order checkout, or filling out a form.
- Platform's technical parameters
Collect stats on parameters of the user's computer: a browser version, operating system, and screen resolution. You need to do it to understand how your site looks on different platforms and optimize for better experience. Also keep in mind that some users can have a slow connection. If it occurs quite often, you'd better minimize the size of your pages.
3. Content.
Whatever the search engine is, content still rules. Priority is always given to sites that provide a complete and relevant answer to a query. What's more, when it comes to content quality, Yandex seems to be even stricter than Google! Especially when it comes to duplicate, over-optimized, and spammy content.

An important point about SEO for Yandex, is that content quality is assessed by at least two algorithms. One of them is AGS filter that was introduced to spot duplicate and low quality content. So, it can be compared to Google's Panda algorithm. Yandex has never revealed what AGS abbreviation means, but many believe that it means "Anti-Shitty-Sites" (if translated from Russian). Well, this is "calling a spade a spade" in action ?.
With its earlier versions, this algo punished sites with thin content by pulling pages out of index. Then, in 2014, it started to nullify TIC (Thematic Index of Citation) of the site. TIC is similar to Google's PageRank.
Yandex uses the TIC score to analyze the authority of a particular site. The score ranges from 0 to 150,000. Thus, when penalized, the site becomes less visible in SERPs, but it is still indexed.
Well, here the best advice will go like this. In order to create quality content, you have to create quality content. There is no other way around this. Of course, quality here means that you are not writing content purely to satisfy SEO search algorithms, but mainly to satisfy users' search intent.
Use valuable internal links that will make visitors stay longer on your site. Plus, link to other authoritative sites to show that your information is valid and valuable.
Give your content a clear structure so that it will be easier to apprehend (and yes, skim), and include visual info like images, infographics, videos, etc.
4. Domain age.

Domain age is a VIP ranking factor in Yandex. It feels good when you have a site with the solid history and reputation, but it is quite cumbersome (to say the least) when you launch a new site, especially when it has few pages. To rank high for a new domain may end up in a massive challenge.
First of all, do not be discouraged if your newly launched site does not achieve high rankings in the organic search. Most probably, you haven't done anything wrong, you just have to wait.
If you are planning to launch a new site, then consider to buy an older domain that from the very start will be viewed as more credible.
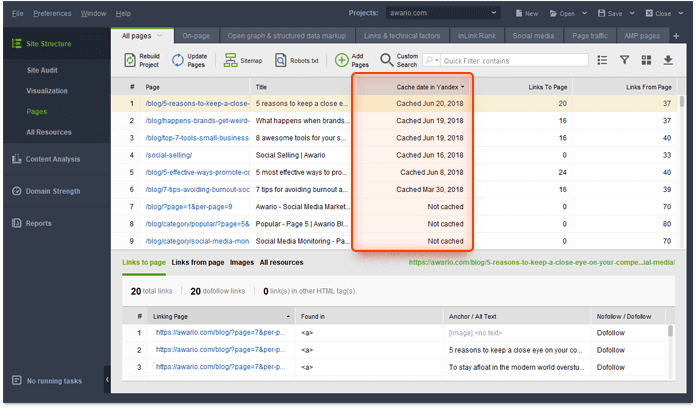
It is possible to check what Yandex believes is the creation date for a particular page by looking at the cache data from the search engine. Use WebSite Auditor, the ideal tool for all things on-page SEO—to do this. It will show you how many pages of your site were indexed by Yandex and when they were indexed.
Download the tool, open it, and create a project for your site. Go to Site Structure > Pages and add the Cache date in Yandex column (by right-clicking the header of any column in your dashboard). Update pages and analyze the results:
5. Commercial factors.

Commercial factors as a part of the ranking mechanism became real in 2011. It was valid first for the Moscow region and then extended to others. Yandex took into account 5 factors that were considered important for commercial websites:
- credibility of the company
- interface
- product range
- prices
- payment methods and delivery
Then, in 2013, Yandex published a document "Quality-biased Ranking for Queries with Commercial Intent" (PDF) where Yandex engineers described the mechanism of commercial ranking. There are 4 indicators of a quality page:
Trustability + Usabililty + Design quality + Service quality
The indicators of trust and service quality have a 2x value comparing to other factors.
The thing is, there are fewer and fewer websites that do not follow the guidelines of this document. It means that if you do not follow them at all, you will lose by default. So you have to tackle the following commercial requirements:
- Detailed contact information
- Company's pages in social media channels
- Detailed product description
- Shipping service
- Customer service (i.e. means of contacting a support team)
- Prices
- Return policy
In order to assess your efforts of a decent presentation of your website's commercial info, you can, first, look at your website as if you are the user or conduct some investigation on how users behave on your site.
And second, you can always look at your competitors, especially in the top 10 of SERPs. Analyze how they optimized their commercial info. The trick here is that in many industries lots of websites are optimized in a very similar way. So, if they are in the top results, by following their lead, you will be on the same level.
6. Meta tags.

Yandex search algorithms pay attention to meta tags similarly to Google, however, Yandex is believed to be much stricter. It can punish the site even for even the smallest mistake with this and on-page SEO. It means that if you optimize your tags, you have to do it in a really thorough way.
There are some things that are peculiar to tags optimization for Yandex. Try to follow them to succeed:
Title and description tags: Titles in Yandex can be slightly longer than in Google, however, to be safe, keep to about 60 characters. Descriptions should be about 160 characters. Like Google, Yandex can neglect your description and show a different chunk of text on the basis of the query.
In case your title and description tags are created automatically, check whether they are of good quality. If they are not, your pages may disappear from SERPs because the search engine has assumed that they are of poor quality.
Meta keywords: Yes, this tag still makes a difference for Yandex. Add a few target keywords per page.
URL: Yandex understands both Cyrillic and Latin characters. Note that Russian-speaking people prefer to use Cyrillic URLs.
Canonical tag: These tags work the same way as in Google, they help to avoid penalties for duplicate content in case you have similar pages. However, if you specify "rel=canonical", it is not an order for Yandex, it can ignore it. The reasons why the search engine won't take this directive into account can be the following:
- The page cannot be accessed for indexing at the canonical address;
- The canonical address refers to a URL in a different domain or subdomain;
- There are a few canonical addresses per page.
Plus, you can check these characteristics with the help of WebSite Auditor. Run the tool and open your project (or create a new one). The tool will analyze your tags on a page basis. Go to Content Analysis > Page Audit. In the Content optimization tab check the Title and Meta tags sections. The Warning and Error statuses require your attention.
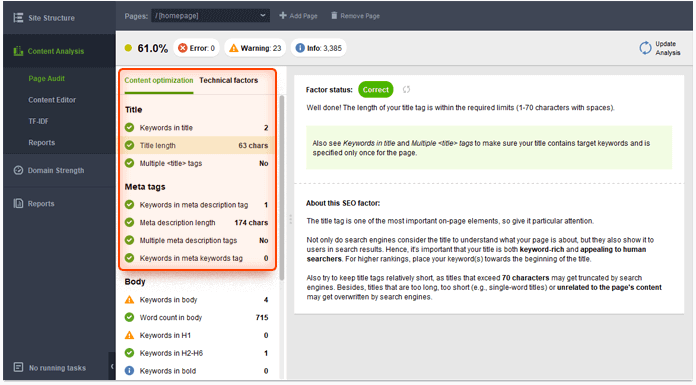
Switch to the Technical factors tab and check your canonicals:
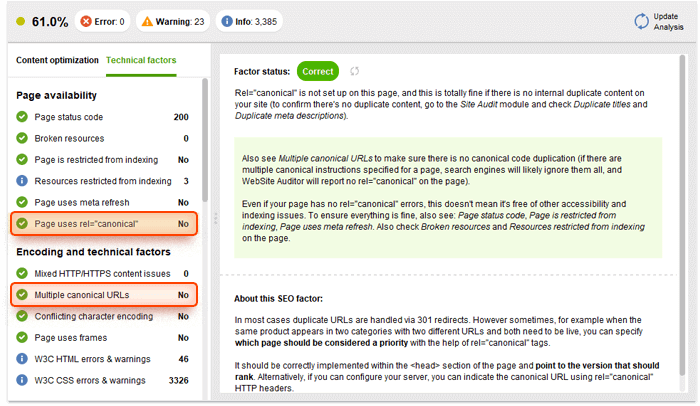
7. Backlinks.
While backlinks mean a lot to Google, it comes as shock that Yandex ended up cutting backlinks from their ranking mechanism. Of course, it does not mean that you do not need to engage into link-building. However, the earned links will have value only if they bring traffic. Otherwise, whatever authoritative a source is, without traffic, it won't make any difference.
What's more, if you try to boost your ranking by means of spam links that are created just to influence the search algorithms, Yandex will find you and will kill you punish you with the help of its Minusinsk algo. It restricts ranking of the sites that use such links for a period from one to several months.
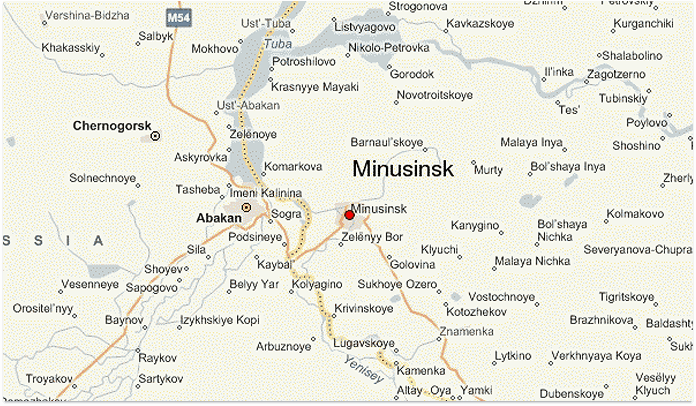
Well, the recommendations for optimization are quite similar to those you use for all search engines:
- Try to earn quality links that will bring traffic to your page. The most plausible way for that is to earn links from the sites that are relevant to your niche.
- Do not buy links in the hope of boosting your rankings, in the end, only behavior factors will determine the value of your link.
8. Mobile friendliness.
Since the end of 2015, Yandex had tagged mobile-friendly sites in SERPs. Such sites were not that numerous (about 18%), but it was the first sign that it was high time to think about mobile optimization.
Then, in February 2016, Yandex launched its search algo update dubbed Vladivostok that regulated mobile search results — sites optimized for mobile started to rank higher.
What's more, in the same 2016, Yandex also launched Turbo pages, a technology similar to AMP in Google. Such pages are adorned with a rocket in mobile SERPs.
The essence of this technology is that mobile pages are kept on Yandex servers that allows for their lightning-like loading (15 times faster for 3G connection!). Moreover, when the site is down for some reason, such pages will still load.
Turbo pages solve the problem of people bouncing off the site when a page loads more than a few seconds. The technology helps to reduce bounce rates at 30%. The best thing for web-masters is that such pages can include ads.
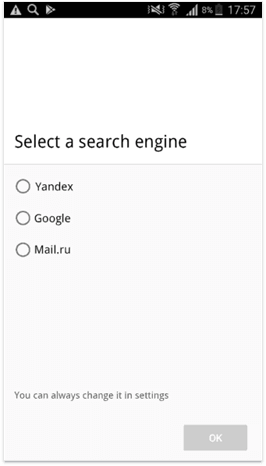
It is also quite curious how Yandex beat Google's mobile search monopoly on the Russian market. The thing is, not so long ago, Android users (that constitute around 70% of the market) could not easily change the default search engine, with Google being the default.
It was ruled out by the Russian Antimonopoly Service that this Android OS default option was too restrictive and not in the interest of consumers. Thus, Android had to make it easier to change the default search engine. This choice screen is now required by law:
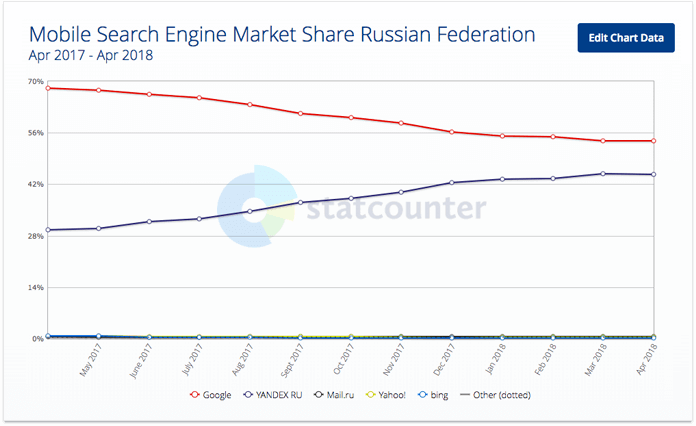
This ruling affected the use stats of Yandex on mobile in a very positive way — from 29 to 44% within one year!
I really hope that your site has a mobile version. Whatever the search engine, these days it is quite necessary, as the numbers of smartphone users are now of an exploding nature.
When it comes to Yandex, you can check your mobile pages for errors with the help of their tool in Yandex Webmaster.
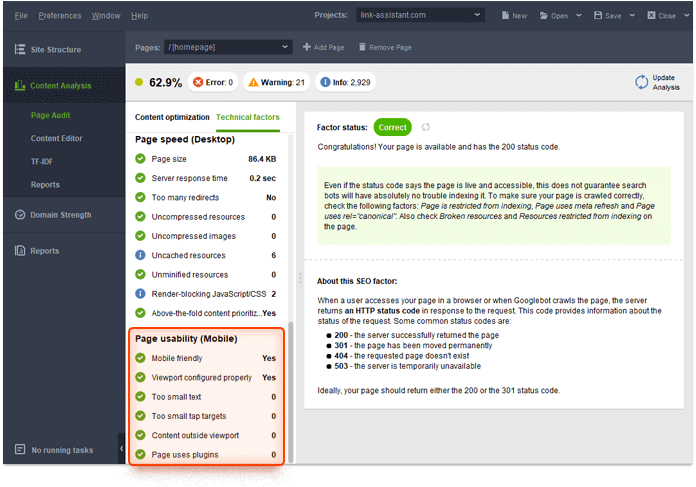
The same check can be run in WebSite Auditor. In the tool, go to Content Analysis > Page Audit and switch to the Technical factors tab. Pay attention to the Page usability (Mobile) section:
If you want your pages to go turbo, check out Yandex's own directions as well as their Debugger tool.
9. Indexing time.
We are totally spoilt by the dynamic nature of Google's search results. Google, being a huge corporation, has the incomparable number of resources that allow for fast indexing of fresh content. It does not work so with Yandex — here the search results are much more static.
The Yandex crawler visits static pages a few times a month and blog posts — several times a day. It means that it can take some time until your content gets indexed.
1) Support the indexing process by submitting new content via an XML sitemap in Yandex Webmaster. Note that there are some limitations that affect how the document is indexed (for example, for Flash files).
2) Be patient and do not give up too soon in case you see no results of your SEO campaign for Yandex.
Afterword: Yandex and AI
Yandex is working hard at solving search intent with more precision by constantly improving their search algorithm. In 2016, they launched their Palekh algo update that used machine learning to handle long-tail queries and find relevant pages even if they did not have words from the query.
In August 2017, they released a new version of the search platform built on the basis of the Palekh neural network. The platform was named Korolyov, after a Russian town northeast of Moscow that has long been the center of Russia's space exploration.

The two major upgrades included:
- Matching the meaning of a query to all the content of a web page (Palekh only considered headlines);
- Looking at a far greater number of pages — 200,000 per search query (Palekh looked at 150 per query).
Korolyov is a far better attempt at matching achievements of Google's RankBrain AI system. Like all modern AI-based platforms, Korolyov teaches itself by processing new data.
Plus, Yandex also announced that data from Yandex.Toloka, a mass-scale crowd-sourced platform for search assessors, would be fed into Yandex MatrixNet (the company's proprietary algorithm), along with anonymized feedback. The data from Toloka (human evaluation of web content) is used to train the machine-learning algorithm.
So, you can judge by the evidence above that Yandex, though very similar to other search engines, is a separate microcosm with its own ecosystem. Once you are inside it, you have to play by its rules. However, when you follow this guide to SEO, you'll better understand the peculiarities—and therefore your SEO campaign for Yandex should be a success.
Are you a Yandex SEO pro? Do you know any more SEO tips and tricks that work for your industry in Yandex? Please share in the comments, I'm looking forward to an interesting discussion!


