10423
•
15-minute read


Putting tons of effort into your site and seeing no traffic is a nightmare for anyone. You choose potentially good topics, hire content writers and SEOs, create high-end designs, and write quality content. Logically, you expect clicks and profits but get nothing instead.
Today, I’ll tell you what are the reasons for the site traffic plateau or decrease. And, of course, show how to fix this and boost your popularity, i.e. get traffic and clicks.
This is one of the most widespread yet fatal mistakes. Your content may be super useful and relevant, but in the world of SEO, it is worth nothing if it doesn’t contain any relevant keywords.
Without keywords, search engines may not be able to understand what your content is about, and thus will not rank it for the desired query. As a result, a page will be sitting idle and not getting traffic.
So, the key points here:
1) If you haven’t done keyword research at all, go and do it asap. Keyword research is a complicated activity, which requires time. But there are tools that can speed the process up and help you find keywords and content ideas. For example, you can use Google Search Console to see the keywords you already rank for.
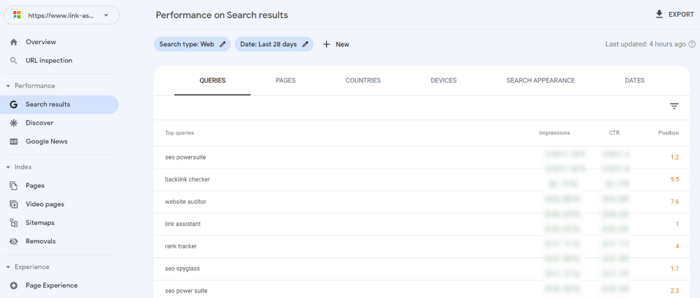
To find new keyword opportunities, you can use Rank Tracker. The tool offers 20+ keyword research methods, so you can use any or all of them if you wish.
For example, here’s how the TF-IDF Explorer module works: you simply add your seed keywords and wait until the tool analyzes your competitors and identifies the most important keywords in your niche.
Download Rank TrackerFind out more ways to do keyword research in our Rank Tracker manual, I’m sure it will be of great help.
2) If you’ve finished your keyword research or done it before, then it’s time to create (or revamp) your keyword map. This will help you identify the best pages for the keywords you’re targeting. You can keep using Rank Tracker for this activity.
Download Rank TrackerOnce you’ve mapped all the keywords to certain landing pages, go to WebSite Auditor and check how well your pages are optimized for the given keywords. You can do this in the Page Audit > Content Editor module.
Download WebSite AuditorPay attention to the optimization rate and follow the tool’s recommendations on additional keywords, alt texts, etc.
Your content may be properly optimized and feature all the keywords you’ve mapped. Still, your pages may not rank well because the chosen keywords are too difficult for your site — say, your SERP competitors are industry moguls with tons of backlinks and high Domain Rank (or DR). If your site does not belong to that highest league, it’s not likely that difficult keywords will bring you traffic.
To check if the keywords you’ve chosen do suit your site scale, go consult the SERP Analysis module in Rank Tracker. Pay attention to Keyword Difficulty and basic characteristics of your SERP competitors.
Download Rank TrackerSERP Analysis is also a source of hints for optimization direction. Look at average SERP metrics and compare them to your page. If the difference is not that huge, you actually have good chances to upscale the page and get into the desired SERP.
Consult the correlation between the SERP position and displayed metrics (Domain InLink Rank, Performance Score, etc.):
These insights may help you see what aspects of your page optimization to tune in order to get into SERPs. For example, if there’s a correlation between the number of backlinks and the position of the page, then you may try to build some backlinks to help your page rank better.
Consult SEO SpyGlass to find new backlink prospects (Domain Comparison > Link Intersection).
If some keywords turn out too difficult, and it feels like you don’t have enough resources to catch up with competitors, then put those keywords aside and consider some less difficult ones. Try those difficult keywords when your site becomes stronger.
If you want to rank for certain keywords, it is important to know what content types these keywords trigger. In other words, you need to understand the search intent behind the keyword. A product page is not likely to rank for a how-to query, no matter how good that page is.
To check what types of content your target SERP features, consult Rank Tracker. Check the SERP Analysis module to see what pages are already present in your SERP and check their content.
Download Rank TrackerOne more useful option is to check the Google SERP Features column in Target Keywords > Rank Tracking. Here you will see what features occupy most of the SERP space and get hints on what content to create to sneak your site into one or several features.
Download Rank TrackerRevamp your keyword map according to what you’ve found.
If you want people to read and share your content, it has to be valuable and useful. You have to tell something new, and present it in a digestible way. If the content is meh, you’re not likely to attract people and traffic with it.
If you want to get traffic, make sure your content solves users’ pains. Study what your audience worries about and explore their interests. Monitor industry events and forum discussions, study reviews, and pay attention to the People also ask section.
Hint. You can search for new hot topics with the help of Rank Tracker’s Related searches and Related questions modules. Enter a couple of your queries and get new suggestions.
Use digestible language, cover all the aspects of the considered topic, and fill your content with numbers and infographics — people like numbers and visualized stats.
Don’t forget to update your content regularly; even topics that seem evergreen are influenced by industry trends and news.
Your site must be properly optimized for search to rank and get traffic. Consequently, your chances of ranking are low if your site is full of technical issues.
The best way to bulk-check your pages and detect any SEO issues is to run a technical SEO audit via WebSite Auditor. The tool will analyze your website and show the results in the Site Structure > Site Audit module.
Download WebSite AuditorWebSite Auditor will spot all the issues related to indexing, redirects, Core Web Vitals, mobile optimization, on-page SEO, localization, etc., and offer you tips on how to fix them.
Google penalties (both algorithmic and manual) may drop rankings of a single page, a group of pages, or a whole website. In the worst scenario, your site may get out of the index. Needless to say that you won’t get any traffic growth in this case.
Google may grant you a manual penalty for black-hat SEO techniques like link juice manipulations, keyword stuffing, deceptive redirects, page cloaking, etc. In addition to manual penalties, Google can penalize your site algorithmically for sitewide technical issues, such as duplicate pages, thin content, redirect issues, and so on.
Manual penalties are easy to spot — go to Google Search Console and see the Manual actions report in the Security & Manual Actions section. In case you’re the “lucky one” with a penalty, you’ll see a notification like this:
Examine the affected page and identify what caused the sanction, fix everything, and request a review.
Things are a bit more complicated with algorithmic penalties, as they are not explicitly listed in GSC. So you have to track Google updates (most algorithmic penalties happen during updates’ rollouts) and monitor your own SEO activity to spot the unproductive move that might have led to downranking.
For your convenience, Rank Tracker has all the Google updates marked on the rank progress graph, so you can easily notice if there is a correlation between your ranking changes and Google updates.
Download Rank TrackerBesides, you can complement the graph with your own activities. Say, you’ve changed your site layout or launched a localized version. Right-click the graph and select Add Event.
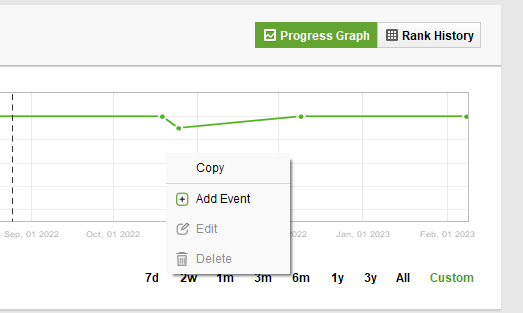
This will help you keep track of your activities and understand what change is to blame for algorithmic penalties if any.
Once the problem is clear, fix the issue on the affected pages and ask Google to reindex your site in Search Console.
Poor UX is a direct way to high bounce rates and low traffic.
When users visit your page and get immediately attacked by annoying pop-ups and banners, their customer journey will likely end without getting started. Bad navigation and slow loading times also negatively affect interaction and increase bounce rates, both on desktop and mobile.
Check your page experience in Google Search Console (Experience). If any URLs have issues, investigate them in more detail:
For a more in-depth analysis, consult the Page Speed module of WebSite Auditor.
Download WebSite AuditorThe tool will welcome you with a full list of affected pages, show what elements cause the problem, and suggest fixing options. All you need is to do the fixing.
Meta elements such as title, description, and structured data are what make your snippets stand out in SERPs. Judging by them, users decide if a page deserves their clicks or not. Logically, if the snippet sucks, it will not get clicks.
Carefully revise all your titles and descriptions. Make them sound attractive and catchy so that users are more likely to click. Avoid clickbaiting — titles and descriptions should clearly demonstrate what the page is about and show its value.
Place keywords closer to the beginning and follow Google’s recommendations on title and description length (60 characters for titles and 160 for descriptions). Although these recommendations are not obligatory, and there’s no physical limit actually, keep in mind that Google can simply not show a part of your title if it exceeds the snippet viewport limit. What’s more, Google has a habit of rewriting titles on its own if it “thinks” that the original one doesn’t reflect the content of the page.
Apply relevant schema markup to make your snippet stand out or even win a rich result like this:
Consult our schema markup guide to implement structured data properly.
To analyze your page’s meta elements, you can go to WebSite Auditor’s Page Audit > Content Audit module. Here you can spot the errors if any, or simply spy on your SERP competitors’ titles and descriptions. And, sure thing, use some of their best practices in your strategy.
Download WebSite AuditorGetting enough traffic without advertising is hard. Especially if your competitors invest in paid promotion and grab the portion of clicks that could have been yours.
The thing is that paid promotion is going through tough times these days — Google and Bing ad revenue reports show a steady decrease and the overall economic prognosis leaves much to be desired.
This revenue decline has resulted in a bid cost decrease. For example, I’ve checked our own ad campaigns and saw a bid price decline of up to 50% in comparison to the same period in previous years. Marketing and SEO agencies around the world report the same situation.
What’s the takeaway? Review your advertising campaigns. It is highly likely that the bids that were too expensive for you earlier are now quite affordable. So you can consider new advertising options.
38% of users quit a website if it looks awful. Logically, there are no chances for traffic and profit growth if your site design hasn’t been updated for ages.
For example, this is how Apple’s homepage looked in 2005:
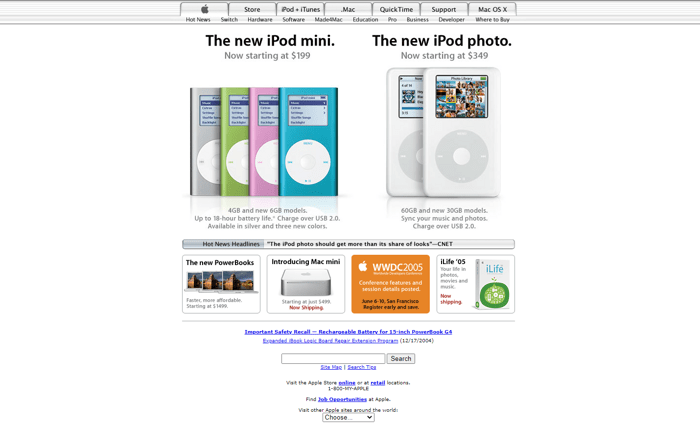
It would hardly be a go these days. So if you haven’t updated your site design for a long time, then go and do it now.
Consider the latest design trends — attractive visual aids can help you more than you may think. Choose appealing colors, and consider what suits your brand and what your audience would appreciate. Use readable fonts and keep design elements in mind.
Sure thing, users are not likely to analyze every design element and consider if it’s good or not, it’s the general experience that matters. Make sure your site is pleasant to look at and interact with.
Social media presence is a must nowadays. Social accounts help build a community around your brand and establish credibility and users’ trust. On social media, people can share and discuss your content. And if you’re not using social media, you miss a fruitful source of traffic.
Keep an eye on your community and take your time growing and managing it. Engage in conversations, answer questions, and post useful and engaging content (and memes). Do not neglect negative comments, too — they may work as a source of content ideas or even product strategy development.
Site traffic is more than SEO. In addition to technical soundness, it’s content adequacy, appealing design, communication style, advertising strategy, and even word-of-mouth. Hope this guide will help you grow your site traffic and attract new paying clientele.
By the way, how do you attract traffiс to your site? What helps you the most? Share your experience in our Facebook group.



