15671
•
9-minute read


As search algorithms grow more and more sophisticated, some people may argue that low-quality backlinks have stopped being an issue as it used to be five years ago or so. A kind of, Google algorithms do all the job, relax.
Yet, the Google Disavow Tool has stayed with us, with a minor update, and link quality is still a ranking factor to consider. So, can we make use of the way Google evaluates links and site authority these days? This article is dedicated to Google's disavow tool and how to stay on the light side in your link-building strategy.
Google Disavow Tool is a way to instruct Google which backlinks to ignore when assessing your site. The disavow tool accepts a file in txt format containing one URL per line.
Once you jump on the page of the disavow links tool, you will immediately see the warning from Google’s team that it’s an advanced feature to be used with caution. “If used incorrectly, this feature can potentially harm your site’s performance in Google Search results.”
This is not because the tool is fragile or will harm your SEO. In most cases, Googlers are sure, their search engine algorithms work efficiently enough to evaluate links and link equity correctly.
Google recommends using the disavow links tool only when you are sure there’s a large number of spammy, low-quality links spoiling your site authority. You cannot use it every other day for several bad links. Using the disavow tool happens once in a while and is a serious action. If you have only several bad backlinks, you are recommended to contact webmasters of these sites first, asking them to remove the links.
The Google Disavow Tool had been a feature of Google Webmaster Tools, and now it’s incorporated in the Google Search Console. The update in November 2020 changed the UI of the Disavow tool, but the principle and functionality have stayed the same.
The Disavow tool is not a 100% guarantee that your site will improve its ranking right after you disavowed all bad backlinks. However, it’s a method to secure against link penalties or unexpected manual actions for something looking suspicious in a site’s linking practices.
And the question many site owners are worried about. If someone puts your site onto the disavow file list, it won’t negatively impact the rankings of your site. The disavow file only tells the algorithms to ignore links pointing to a site. As for collecting data from the disavow tool to find spam sites and penalize them — Google representatives assure they don't use it.
You definitely know that backlinks are a strong ranking factor for Google. Backlinks serve as a signal that your site has valuable information for users, so the presence of quality backlinks increases the overall domain authority.
According to Google’s definition, low quality links are
Any links intended to manipulate PageRank or a site's ranking in Google search results may be considered part of a link scheme and a violation of Google's Webmaster Guidelines. This includes any behavior that manipulates links to your site or outgoing links from your site.
Life would’ve been too simple without people being so inventive, trying to deceive all kinds of rules. That’s how negative SEO practices appeared at the very dawn of PageRank and DA estimation. Artificial, low-quality links, aimed to manipulate domain authority and PageRank, started to be cheap marketing goods. Which made Google create the Penguin algorithm to demote sites for manipulating ranks. Soon after the Google Penguin algorithm was introduced (that was in 2012), the Disavow Tool was launched to help SEOs help Google estimate backlinks and sieve away spam backlinks.
One should know the difference between algorithmic penalties and manual penalties, handed over by Google. Algorithmic penalties are regular internal workings of Google’s core (the Penguin algorithm has been part of the core Google algorithm since 2016 which means it's now real-time and imposes and removes penalties quicker).
Whereas manual actions are imposed by human reviewers when they notice that some site manipulates link equity with negative SEO tactics. Usually, you will find a notification in your Search Console about a manual action being applied to the website for some indicated reason. While with algorithmic penalties, you can only guess.
A classic example of recovering from a manual action discussed in the webmasters forum: someone scrapes your content and creates a duplicate on a single-post website. Why they do it? To hurt your rankings or feelings, or both. Wait for no mercy from Google, although it’s just a third-party negative SEO attack with bad links.

This used to be a dirt-cheap method to insert an absolutely free link in forums and blogs, so spam comments proliferated like fungus. Comment spam became so commonplace that many site owners simply closed all user comments with nofollow tags. Eventually, the UGC tag appeared for user-generated content. So, comments kind of don’t count, although it still depends on how website editors moderate comments.
This type of content promotion is pretty popular to raise brand awareness and improve SEO. But sometimes, it may have an adverse impact if the agency providing such services goes a bit astray. While you have control of your content, make sure it is high-quality, linkable and clickable. Or else you may have a tough time trying to remove all those duplicates and thin content off the web.
Links in the footer of a free WordPress template used to be a good source for links and credits to the author who modified it a bit, but it’s no longer as such. Avoid getting massive links from templates and author profiles, as it’s a clear signal to Google the links are unnatural.
Link exchanges in the form of link farms (typically created by automatized tools) were quickly classified by Google as spam and devalued. The Panda algorithm update hit private blogger networks (PBNs). These are sites that are mutually promoting. The reason for penalizing them is usually thin content and link schemes.
What Google wants is that all sponsored content should be marked accordingly. What Google cannot control is paid links in the content, unless they turn too massive and explicit. This shadowy side of web earnings is still prospering. However, if caught red-handed — usually thanks to a disproportionate flow of inbound or outbound links to sites irrelevant to your general content — the manual penalty is guaranteed.
There is a trick of hunting expired domains: find one with a good link profile, and get a lively start when launching a website. Well, a good new domain is quite hard to get, you still need to check its link profile. Just make sure that it hasn’t been abandoned for having too many link penalties to deal with.
Well, first of all, how do you know that some low-quality backlinks hit your site? That’s where link auditing comes into play. In fact, a regular link audit should become part-and-parcel for the backlink strategy of any living website.
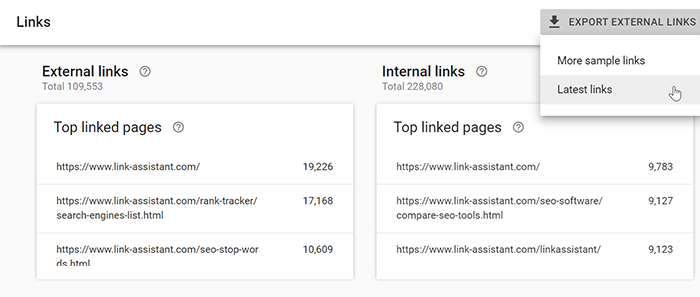
For a quick link audit, go to Google Search Console > Links module, where you will see your top linking domains, backlinks and anchors. This overview will give you a general understanding of how strong your site’s link profile is.
Currently, the Search Console won’t let you download all the links found in your backlink profile, only around 40% of it. For example, it shows over 100,000 external links in my Search Console. But as I go to Export External Links > Latest Links, I find only 43,000 backlinks on the CSV list I downloaded.
You can also try downloading More Sample Links and combining those two, but these lists look approximately the same, the former being truncated and sorted by the discovery date. This is because the Google settings limit link extraction up to 100,000 rows.
Still, the issue of analyzing backlinks is open. First, we might miss those links that actually bring us a problem. Second, how shall I check the quality of those backlinks? When there are hundreds and thousands of them, how can I evaluate them to know there’re link penalties looming large? Which brings us to...
Alternatively, you can try a backlink checker tool to audit the link profile of your site. Usually, such tools run some estimation features that let you evaluate your backlinks quality.
Let’s try to see how to do this with SEO SpyGlass backlink checker. First, you need to download the application and run for installation, it won’t take you long. Then, start the tool and paste the URL of the site that you want to examine for backlinks. Proceed with the instructions to complete project creation. In a couple of minutes, the software will analyze your backlink profile and return you results with thousands of backlinks.
How do you know which of the backlinks aren’t good? To estimate the backlink quality and the chances for link penalties, there’s the Penalty Risk score.
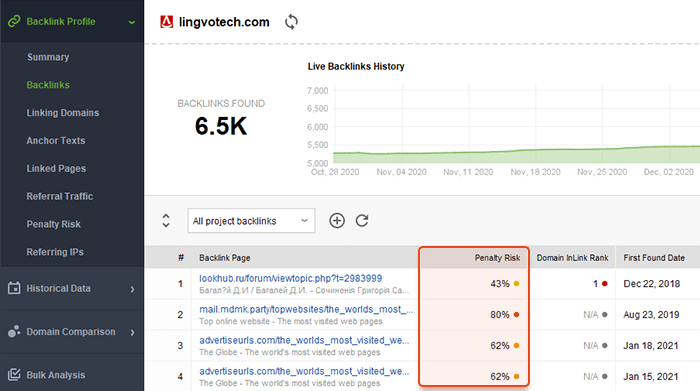
If the column is not available in the table, click on the icon in the top right corner to Edit Visible Columns and check the Penalty Risk column to be visible in your current workspace.
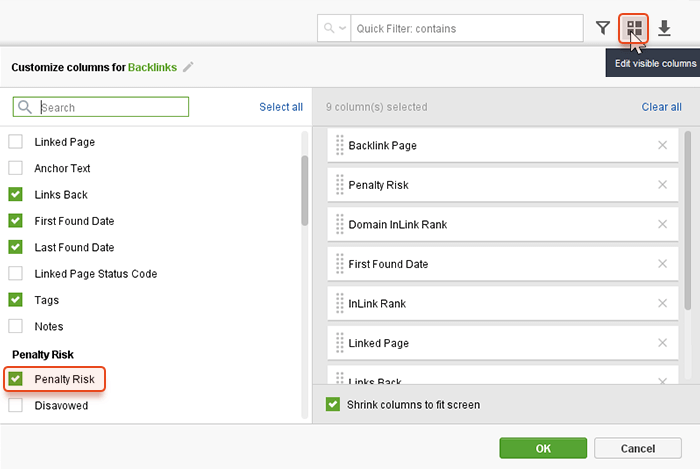
Click on the Info icon in the backlink row, and you will get a tooltip about the penalty risk factors, detected for this link.
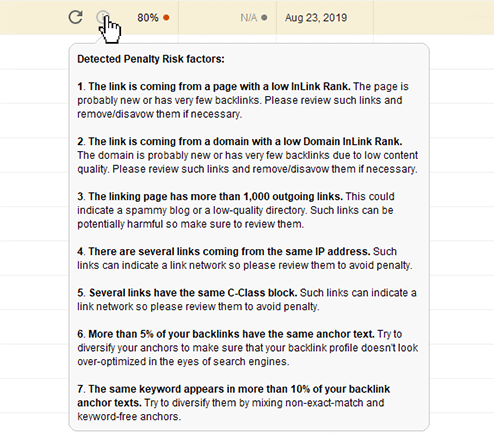
If there are only a few backlinks looking risky, probably that’s okay. You can check the linking site manually, and if you find this to be a trusted domain, you may leave it as it is.
Besides the Penalty Risk score, there will be several other signals that the site might be spammy, like:
• Low Domain InLink Rank.
• Strange-looking TLD.
• No social activity across the domain.
When you’ve found lots of spammy links that might disrupt your site authority, you should take measures to avoid Google penalties.
Before using the Google Disavow Tool, try contacting the webmaster of the linking domain and ask them to remove the bad links.
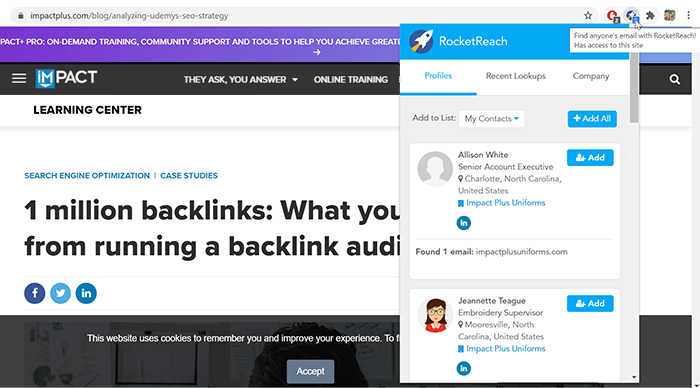
Sometimes, bad link removal might be an issue, especially when you have lots of spam domains to get rid of. When you need to find lots of emails at once, some automatized email lookup tools will save you tons of time and energy.
For a start, there is the Rocketreach plugin which you can install in your browser and search for the contacts just as you proceed to the site and look for the contacts. That will be just a bit quicker.
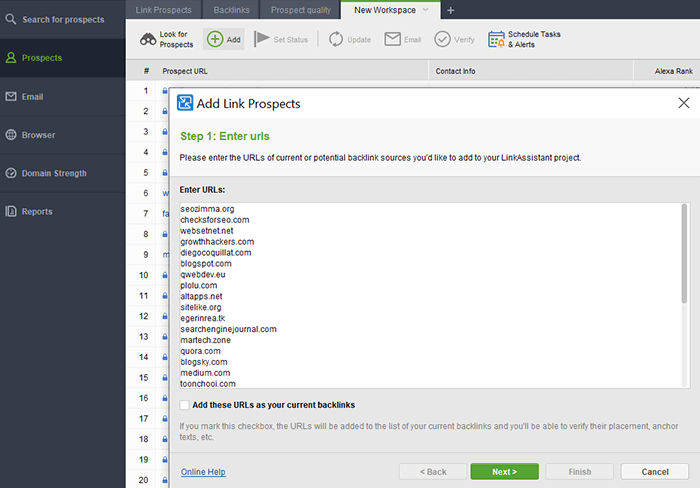
As an alternative, you can run the Link-Assistant outreach software. For your existing disavow list of domains that you want to remove from backlinks, copy the list from SEO SpyGlass and paste it into LinkAssistant.
Step 1. Go to Prospects module and click the Add button.
Step 2. In the pop-up window, paste the domains that you want to find contacts for.
Step 3. Hit Next and add a comment to be applied next to these prospects, this way it will be quicker for you to filter the prospects within a larger list.
Step 4. Hit Next and check only Contact Info button to update. The software will collect all publicly available emails from the domains.
Once you’ve collected all the emails you need, reach out to them right in LinkAssistant. Right-click on the list of prospects you’ve researched and choose Send Emails to Selected Participants (notice, that before that action, you have to define the email client for LinkAssistant).
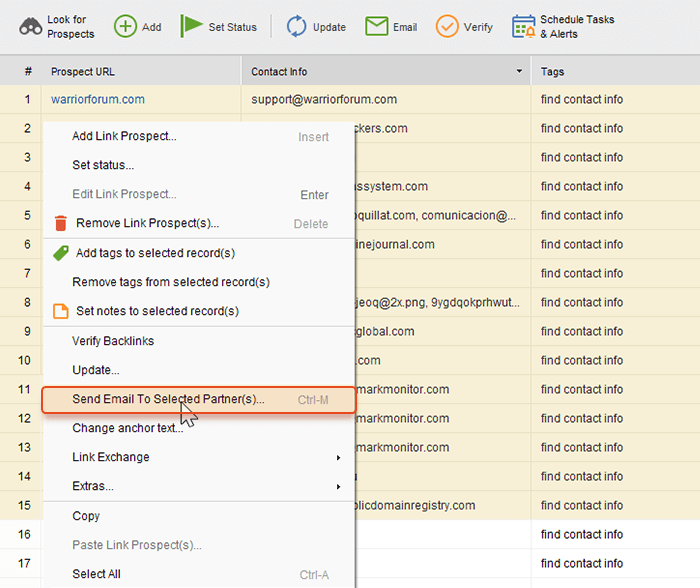
There’s a template email titled ‘Link Removal Request’ (which you can edit and modify to give it your personal style). Send the bulk email asking them to remove the spammy links.
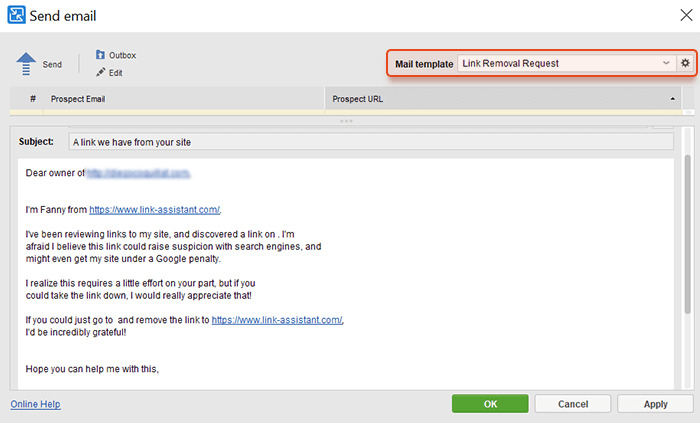
And in case those webmasters of bad linking domains won’t listen (very often, they won’t answer), there’s nothing left for you but to use Google’s Disavow Links Tool.
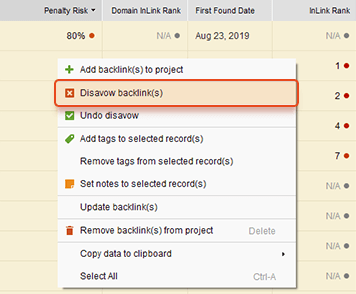
Compiling a disavow file in SEO SpyGlass is super easy. Double-click on the Penalty Risk header to filter the backlink rows and to show the links with the worst score at the top. Select those backlinks and right-click on them to call the context menu where you choose the Disavow Backlinks command.
The pop-up window will appear where you can choose an option to disavow either specific backlinks or the whole domains. And leave a comment about the disavow action, for example, specify the reason why you decided to disavow them.
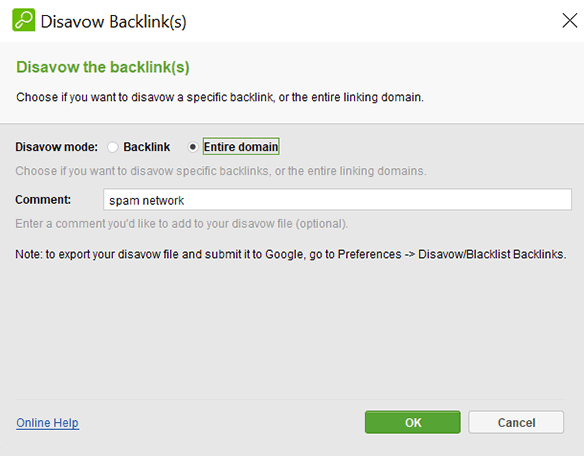
Then go to Preferences > Disavow/Blacklist Backlinks to open the disavow module. Here you will have the whole disavow list of backlinks ready to be exported.
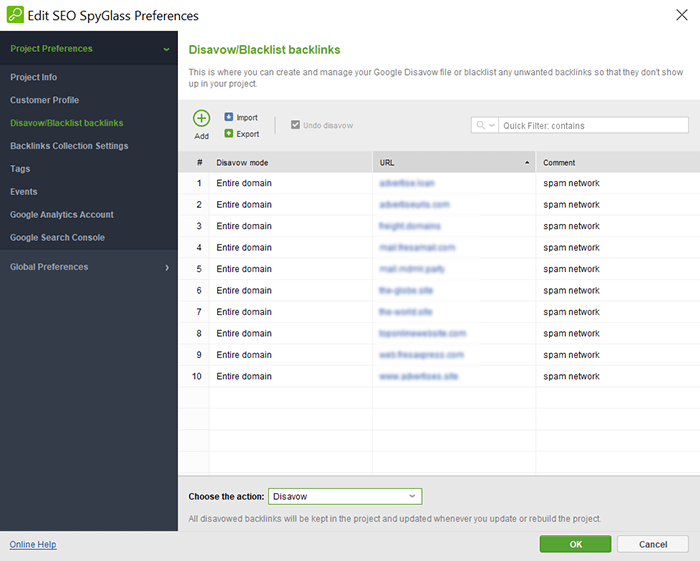
Select Export, and you will be offered to save the disavow file in TXT format. The list of the domains, together with your comments to them, will be saved in domain:domain name format.
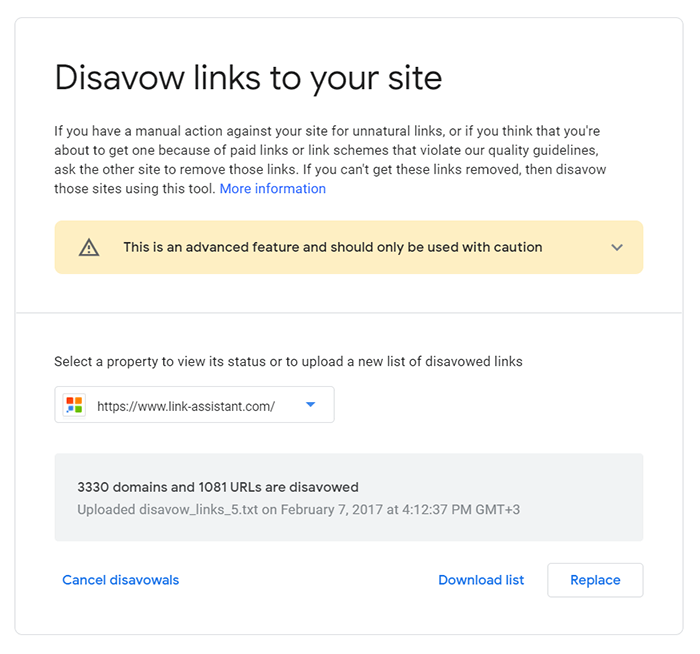
When your TXT file is ready, go to the disavow links tool page and select the property for which you are disavowing links. Proceed with the instructions to submit your list.
The whole disavowal process may take a while, and sometimes people are worried if the list has been actually considered. This is because the bad links will still stay in your link profile in Search Console.
When Google recrawls your site next time, will it still see the disavowed backlinks? Disavowing links is not the same as removing them. The spam sites keep linking to your site, however, Google algorithms ignore these bad links. If they really did harm to your site authority, its rankings will improve after disavowal.
For a disavowed links audit, the current version of the Google disavow tool allows downloading the list. You can have only one disavow file at a time in the tool dashboard, so, if you need to add more bad links for disavowal, just replace the old list with an updated one.
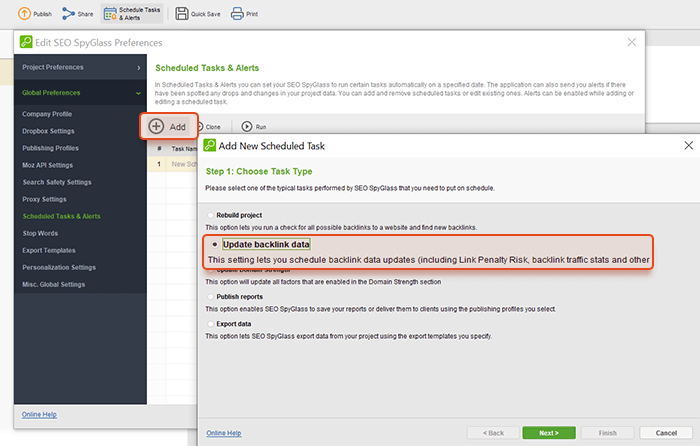
Link audits will help you have a clean link profile. With SEO Spyglass professional features, you can set the tool to do the auditing task regularly by itself. In the top right corner (or from Preferences) go to the Schedule Tasks and Alerts module and add the task to update the backlink check.
Pick the frequency how often you need the link audit, and define the delivery method for the results (as for me, it’s convenient to have it in the email). You can modify the report to include only the data you need, for example, the new backlinks, their URL, penalty score and referral traffic.
Besides, there’s a nice trick to set an alert in case something extraordinary happens. Having an unexpected backlinks surge at a time may be a signal of an SEO attack. Better safe than sorry, as they say.
I'm gonna secure my site with Scheduling Tasks and Alerts fetaure in SEO SpyGlass.
Step 1. Right-click on the task for Update Backlink Profile and choose to Edit scheduled task.
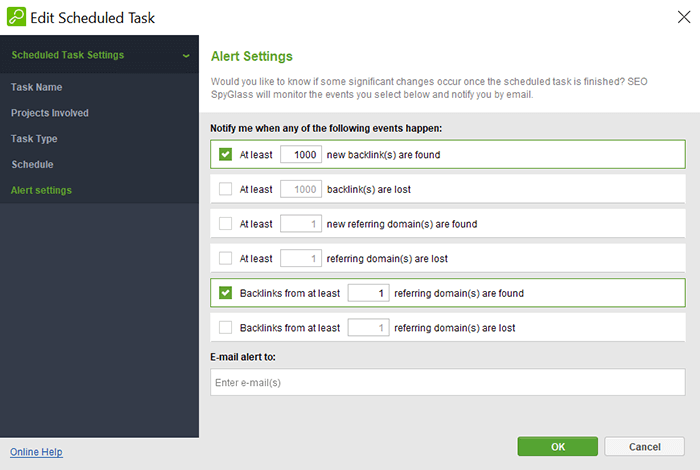
Step 2. In the next window, go to Alert Settings and define the conditions for your alert. For example, a sign for an SEO attack with bad links could be having too many backlinks from only a few domains.
Step 3. Enter the email where to deliver the alert, press OK, and you are safe.
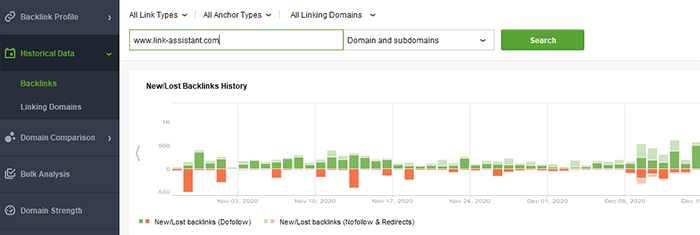
By the way, in the Historical Data module, find out the general picture of your regular backlink influx and what is considered normal for your site.
Why care for link-building? First, everybody does it, second, what else should we do? Take care of your backlinks just because it lets you build the kind of backlink profile you want.
The point is that you still can do link-building outreach in the right way. You still can look for your niche marketing pals to run advertising campaigns, to do a bit of affiliate marketing and guest posting. If you pick the right sites that are relevant to your topic, you coin partnerships which are good not only for your SEO, but for business overall. And in between, you still have control over the content and anchor text diversity… So, don’t miss our guide on the best link-building practices for local SEO.
Have you ever used the Google Disavow Tool? Please, share your stories in the comments!



