3 Tips to Use Google Analytics to Improve SEO

Even if you’re new to SEO, you’ll quickly realize it’s impossible to properly apply your strategy without diving into the many options that the Google Analytics platform has to offer. For example, you can focus on writing eye-catching blogs that convert well, but you’ll never know how successful they were if you miss out on the actual conversion rate.
If you spend some time playing around with different sets of information about your visitors, you’ll see it’s fairly easy to get overwhelmed with the amount of available data. Gathering insights such as users’ location, interests, or how much time they spend on a page is just a fraction of it.
The way visitors engage with your website leads to more useful insights that can help you determine what you need to improve. Some examples include Behavior flow, that shows how they navigate the pages, or the Content section that shows you what’s popular with your audience.
Let’s go over some tips that can help you make sense of the process and work on increasing your website ranking.
1. Determine traffic sources
Before you start adjusting your SEO strategy, it’s important to figure out which of your sources perform the best so you know what you can focus on. The best place to start is the Channel Grouping report that you can access by going to the Acquisition panel, choosing All Traffic and picking Channels.
This is a point you’ll come back to often, as it allows you to see all of the sources, as well as other important insights such as keywords that are driving the most traffic.
Attribution modeling is a great way to analyze the quality of traffic you’re getting, volume levels coming from different channels and determine how to proceed based on the insights.
There are various default attribution models that you can use depending on your objectives, each allowing you to focus on a different part of the cycle. Even though you can create custom models, the last interaction model is one of the easiest ways to see the direct step that a user took before making a conversion. By attributing the complete conversion value to that last channel before they converted, you can determine how successful your organic efforts are and what’s worth the further investment.
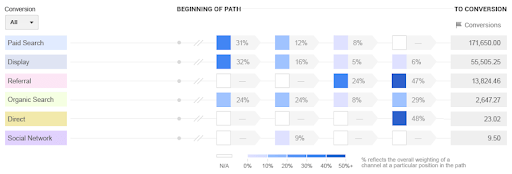
Other models can also help you determine if your content is giving results throughout the cycle. For example, the Linear model can be useful when your goal is maintaining awareness and show how you’re doing with each touchpoint. Last Google Ads Click one can also be great when you’re testing different Google Ads API options.
Lastly, keep an eye on your backlinks, as you’ll have a stronger understanding of the referral sites that give you traffic and can double down on creating similar content.
2. Set SEO-focused goals
Tracking your traffic is essential, but by just following the numbers and not making a difference between results you won’t necessarily get enough information on how to assess your metrics and what to improve.
When you add the tracking code in your Google Analytics account, you can also set specific goals from the admin panel to reflect what you want to achieve with your SEO strategy and make all of the KPIs easily measured.
Whether you’re looking for visitors to add a product to their cart or subscribe to a newsletter, it’s all about conversions. When you keep track of the number of users and the conversion rate, you can track how changes on your corresponding pages impact the results.
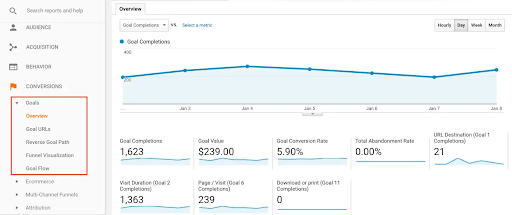
This also allows you to get specific. For example, set leads generated from organic traffic as a goal. You’ll now have an overview of the ranking of your pages, as well as the visitors’ quality.
After that, creating a dashboard with the most important widgets will make your analysis much simpler. You can include just a few most important ones to start – total organic visits (Medium/Exactly Matching), goal completions (Keyword/Sessions) and top organic keywords and the percentage of new visits.
3. Dive deeper into page performance
You can take a closer look at your landing pages by going to the Behavior panel and choosing the view from Site Content. From there, you can compare different periods to see trends for each page.
This can help you find out if you have more content or technical problems – if a single landing page has a substantial drop for the period while others are doing fine, it may indicate that you need to do some updates there. It can also show an overall negative trend which means that you should probably take a look at the issue from a more technical standpoint.
For example, if your bounce rate is over 40%, the configuration of the page might be wrong and that’s causing issues with the visitors, such as slow loading time or misleading titles.
Of course, this is far more concerning if the bounces are happening on a page such as the checkout or a product page than on a single-page content such as a blog post.
Your monitoring should also include alerts about important performance drops and website issues. You can set them up from the admin panel and one of the best ways to approach this is by creating an alert that will be activated after a certain spike in organic traffic in a specific timeframe, both negative and positive.
For example, more than 25% decrease and 35% increase between two weeks is a range that can be enough to start but can be adapted to the nature of your brand.
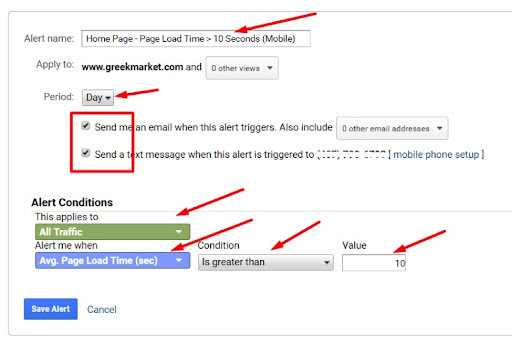
This can help in both replicating successes with relevant keywords when the change is positive or noticing that you’re ranking for irrelevant ones on time.
Another alert that’s great to have is for 404 pages – especially if you have a large website. That way you’ll resolve the errors more efficiently and avoid an increase in bounce rate.
Summing it up
Google Analytics offers quite a few ways to segment data. The best way to start is by filtering your traffic sources. When you understand where the users are coming from, you can then start noticing the volume and the traffic quality as well.
Try finding the most efficient way to label the different channels, as you’ll need to keep track of various ways the users end up seeing your content.
After that, it’s a good idea to create specific goals in line with your SEO strategy and track them with a dashboard. It can take some time to create a perfect mix of widgets but try not to go all-out and instead stick with the ones that are truly relevant to you. Finally, always keep looking for ways to improve your landing pages and take notice of changes, both negative and positive. When you have proper systems in place for tracking them, it’ll be easier to adapt and react to make necessary adjustments efficiently.







