22937
•
11-minute read


Some SEO topics are speculative, and keyword cannibalization is one of them. Different opinions exist: some people say it is a serious issue that can lead to sudden ranking drops, whereas others are not even sure about its existence.
So, what is keyword cannibalization? Does it really impact a website's ranking? Let's take a closer look at the phenomenon and find out when it is an issue and when it is not. In case it is, we should know how to detect and fix it.
Keyword cannibalization is a ranking issue when several pages from the same website compete in search results for one keyword, hurting each other’s ranks.
Keyword cannibalization occurs when different pages are optimized for the same or similar queries, and Google cannot identify which of them is more relevant. As a result, these pages compete with one another in organic results, and none of them can get to the top positions.
The SEO term was coined from the marketing concept of product cannibalization: this is when a company loses in sales because it has introduced a new product, replacing an older one.
The term appeared in the early era of search optimization when SEOs believed that it would be easier for their websites to rank if they created many pages targeting the same keyword.
Further on, Google introduced several updates, one of them called the Site Diversity Update, seeking to limit the presence of a single domain in one SERP. This improvement aimed to diversify search results and increase organic competition.
At present, host crowding and domain clustering filters prevent multiple same-domain pages from appearing in the organic listings. In the past, you could find five pages from the same domain in the top 10. Today, Google shows two pages from the same domain on a SERP, in rare cases a little more.
If you run the query search and append the &filter=0 to the URL of the Google search page, you will disable Google’s domain crowding filter. For example, here I look up the ‘on-page SEO tool’ and find the domain of SEJ on page 3. And with the filter disabled, I can find three more pages of this domain corresponding to the same topic on page 8.
Today, search engines can define quite precisely what a page is about. Moreover, search engines go far beyond keyword density, guessing the search intent and pages’ relevance to a query. If Google finds several relevant articles on the same website, it will show them in the SERP. But would those pages cannibalize each other? Well, it depends.
There are cases when two pages may show up on the first SERP, but it will not be keyword cannibalization because there is no conflict or ranking issue.
An average page occupying the first position on a SERP for a popular keyword can also rank for about a hundred other keywords. No wonder the landing page may intersect with other same-domain pages targeting similar or the same keywords.
If we check the SERPs for a ‘rank tracker’, we may find many examples of multiple pages from one site very well positioned for the same (and quite competitive) keywords.
As you can see, the pages are ranked second and third on the first SERP. Google has picked the most relevant pages that are complementary. They both meet transactional intent but are different by page type and serve slightly different purposes.
Here is another typical example of when a blog post and a product landing appear together at the top of the SERP. This is host group, two indented results with consecutive pages written about the same topic, but targeting a different intent. The article about how to use the tool is more descriptive and supplementary, but still relevant for this very query, so it goes just after the product page (in addition to the video results located above). So, this is not keyword cannibalization either.
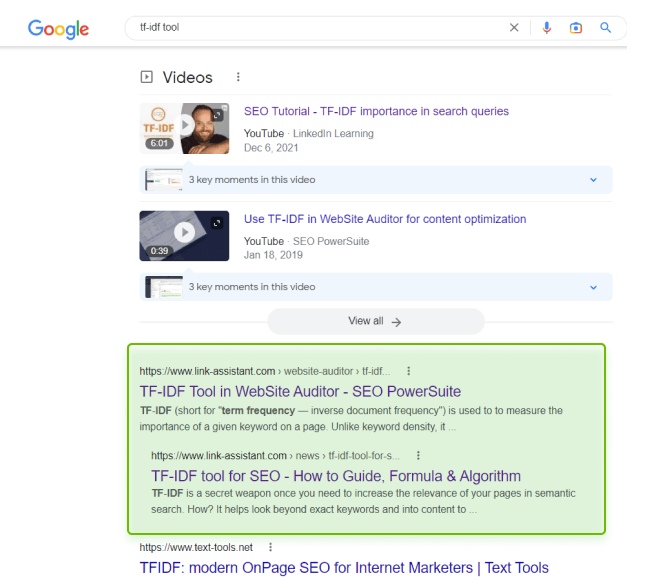
One more example shows several same-level pages ranking for the same keyword in e-commerce.
And one more example of the homepage and supporting resource showing up together in the SERP.
So, you can easily have several pages occupying the top positions on a SERP. And this would not harm your website. Instead, the situation as such is likely to boost your site visibility, attract more traffic to your website, and improve CTR.
If it's your case, congratulations because you have that big traffic-gaining chunk of the SERP, and there is nothing about keyword cannibalization here.
Now, let's look at the cases of keyword cannibalization that turn out to be a problem that ruins SEO efforts. In such cases, your ranks may suffer as well as CTR, conversions, and other crucial site metrics. The most dangerous thing about keyword cannibalization is that it is hard to notice it immediately.
The simplest way is to run the site: search for your keyword. Google will show all your site’s pages drawn into the SERP by this query. Take notice of the URLs with similar titles and content.
Once again, you can search for your keyword and remove the domain clustering filter, setting the value to &filter=0 with the search. It will reveal more pages in the SERP triggered by the query. This can be a clue to where to make changes for each page to start showing up on its own.
If you need supportive evidence to prove keyword cannibalization is in action, you can check your ranks and spot cases when multiple pages are ranking for the same queries. Next, you should find out whether the pages hurt each one’s ranking.
Briefly, you will be looking for multiple pages ranking quite low for the same query in the SERPs and changing their positions frequently.
This task may look somewhat complicated unless you have a ranking tool for it, for example, Rank Tracker.
Step 1. Find multiple pages ranking for the same keyword.
You may have decided that certain pages should rank for your target keyword. But Google may decide otherwise. It may see other pages as relevant to the query in addition to your landing page. The keyword cannibalization tool will help you discover such situations.
Getting back to the point where we started, not all cases of multiple pages ranking for the same keyword will be about cannibalization. Most often, they will be enriched results that make your site stand out on the SERP. This often happens in the first top 10 positions.
Instead, we need to focus on underperforming pages which you want to get into the top 10. If your pages compete with each other, they will rank low and even flip-flop positions for the same keyword.
Step 2. Observe which pages swap positions frequently.
At this step, you will need the Keyword Mapping tool in Rank Tracker to match your landing pages and target keywords (or a group of keywords).
To map a keyword, right-click on it and choose Assign selected keyword(s) to landing page. You will find the mapped pairs in the Rank Tracking > Keyword Map module. You can also add a column for assigned pages in your Ranking details workspace.
Once you map some keywords, you can see if other pages rank better or instead of the mapped landing pages. An orange warning sign will appear next to your Ranking URL. With each check-up, the keyword cannibalization tool will notify you if the ranking page suddenly becomes different from the one you have mapped as your landing page.
Download Rank TrackerOver a few months, you will have accumulated a history of your rankings, which you can check in the Rank Progress > Progress bar at the bottom of the workspace. The ranking progress graph will be uneven because the pages struggle to rank for the keyword, but quite unsuccessfully. Here is an example when several pages's rankings suffer from cannibalization.
Download Rank TrackerHow do I know which page entered or left the top? To find this information, switch to Rank History and look through all the pages you’ve found ranking and their positions.
Download Rank TrackerThe example above shows how a product page ranked for the target keyword. However, a ranking help page replaced it and, in the end, has given way to a how-to guide. In this case, we should to recheck what's happening on the pages, which brings us to the next step.
Step 3. Analyze keywords and search intent.
To prevent keyword cannibalization in SEO, we must always consider the search intent of our target keywords.
There are at least three intents critical to SEO: informational, investigational, and transactional. Although we could extend the list to numerous microintents, let's skip the nuances here. Our task is to understand what kind of intent stands behind the query of interest. We may have our guesses but we can also see how Google understands the intent of a page.
In practice, we need to tweak the SERP and see what kinds of pages are the most successful for our query. Is it a blog post, a listicle, or a product page? Is it aimed at informing the searcher or helping them to make a choice? Of course, you can check the SERP manually, but there are some nice tools that will help you analyze the SERP quicker.
To see the SERP, check the results manually or scan with Rank Tracker’s SERP Analysis. The latter will reveal not only your competitors but also keyword difficulty and important SEO stats, such as links, page speed, and domain authority.
Download Rank TrackerAlternatively, use WebSite Auditor’s Content Editor. The tool will list your competitors, and you can even preview their articles right in-app. Content Editor will also suggest topics and questions from the People Also Ask box triggered by the query.
Download WebSite AuditorNext, analyze the page that is downranked due to keyword cannibalization. First, ask yourself whether the content format is suitable. Does it convey the intended message clearly? Does it cover the topic in a way that meets the searcher’s purpose?
Finally, find the page’s ranking keywords that, probably, bring traffic additionally. You can check it in Google Search Console in the Search results section. Filter the URL you are interested in and see its top queries.
Alternatively, there is a quick way to look up a URL’s ranking keywords in Rank Tracker > Keyword Research module. Choose Ranking keywords, paste your target URL and set the tool to research the exact URL, define other settings relevant to your investigation, and hit Search. You will see all important keywords, the position the page takes on Google for each query, the organic traffic it has brought over the month, etc.
Download Rank TrackerWith all this, you will be able to figure out whether it is better to keep the page, delete, or re-optimize it.
There are several ways to fix SEO content cannibalization. You might need to use any of those that suit your case or combine different methods.
This method fits when you have several pages on the same topic. Analyze their content to select interesting details on each page. Then rewrite the landing, taking the most useful content and merging these pages into a better in-depth piece.
You may delete the some of the cannibalized pages. However, if they have some ranking power, it’s better to set up proper redirects to the new landing page.
To make your landing page more relevant to the target keyword, use SEO writing tools to increase their chances for optimization success. Content Editor in WebSite Auditor is a nice solution to help you do this. Just paste your existing URL or add a new one and paste the target keyword. Content Editor will give you all the helpful data based on the competitive analysis of the top 10 ranking results.
In this content writing tool, you’ll get:
Internal linking is crucial for getting SEO done right. It shapes a website structure and helps search engines better understand the importance of site pages. The more backlinks a page has, the more prominent it seems.
You can audit your site architecture in WebSite Auditor with its interactive site visualization tool. It will help you grasp the entire structure of your site and pinpoint issues in a moment.
Download WebSite AuditorThe Visualization will let you quickly overview your pages' hierarchy. Here, you can see how your pages link to each other and find all the redirects or orphan pages. You should ensure that your landing pages have enough internal links with relevant keyword-based anchors.
Moreover, here you can map your implemented or future redirects, annotate changes, and see how the pages’ prominence would change. Just in case you are interested, this website structure visualization guide explains how to build an SEO-friendly site structure.
Duplication issues are not strictly about keyword cannibalization as such, but it works similarly: search engines cannot figure out which page to show out of several identical. Of course, Google may try to identify which page is the main one. But it will also take a bit longer for Google to discover and sort out all these duplicated pages.
Make certain that your site is clean from duplicate issues by auditing it in WebSite Auditor. Check out the Site Audit > On-page section.
Download WebSite AuditorIn certain cases, often happening on e-commerce or multi-locale websites, duplicate content can be fixed by canonicalization. The rel="canonical" tag tells search engines which page from several duplicates to show in the SERP. Moreover, the canonical tag consolidates link signals for similar pages into a single URL.
Thus, make sure to use the right canonicals to show search engines which pages you want to appear in the search results. Here Google provides detailed instructions on how to define canonicals.
Let's take a closer look at the negative aspects of keyword cannibalization. So, why is keyword cannibalization so bad for SEO? Some of the reasons are that it leads to:
This negative impact will eventually make your SEO efforts just a waste of time and resources. So, the best approach here is to audit your pages for cannibalization issues, fix them, and try to prevent them in the future.
Whether you are just starting to build a website or thinking about creating a new page, you need to foresee cannibalization occurrences at the very beginning. SEO PowerSuite tools have some awesome features to help you prevent keyword cannibalization issues. Below are some ways to deal with it.
1. Research keywords with a focus on intent.
So when you search for target keywords for a new landing page, think about what intent a chosen keyword bears. In the process of creating new content, make sure to cover this intent. This will increase the probability that the landing page will be found relevant for this keyword.
2. Analyze SERPs for intent and ranking factors.
SERP analysis is closely connected with the previous point. Before creating a piece of content for a landing page, analyze the SERP for the target keywords. This step will save you lots of time and effort in the future.
Examine what types of content are shown at large for a given keyword. What intent does it cover? No wonder it would be hard to rank well for an informational search query if your content covers transactional intent, etc.
3. Track keyword positions.
Keyword mapping is an often underrated but great solution. Together with a content strategy, it may help you prevent keyword cannibalization and understand what content you will need to create in the future.
You may use a keyword mapping spreadsheet with your existing pages and assigned keywords, combining them with a content plan.
Or, to make it simpler, use keyword mapping in Rank Tracker and the Automated Tasks and Alerts scheduler. Set up automatic rankings checks, and the keyword cannibalization tool will take care of your daily routine and put your efforts to the minimum.
4. Audit your site regularly.
Site issues are generally a heavy drawback for SEO. WebSite Auditor lets you run regular site audits: just set up an automated task to run a check-up on autopilot, and the tool will scan your site and even deliver the report to your inbox. As for keyword cannibalization, pay attention to duplicate issues, site structure, internal links, and anchor texts.
To sum up all of the above, here are the essentials of keyword cannibalization:
1. Multiple pages ranking low for the same query, and whose rankings fluctuate heavily, is a sign of keyword cannibalization.
2. Keyword cannibalization is hard to detect, but with position tracking, it can be done faster.
3. To prevent keyword cannibalization, focus on intent-based keyword optimization and audit your site’s SEO health regularly.
Even with high-quality content, all efforts may go awry with keyword cannibalization issues. This is not something on the surface, and losses may come unnoticed for quite a while. So, stick to thoughtful keyword planning, check SERPs, and audit your content regularly, and keyword cannibalization will never happen.